Unlocking the Potential of Laboratory Ultrapure Water Systems: A Comprehensive Guide
Time:
Dec 25,2025
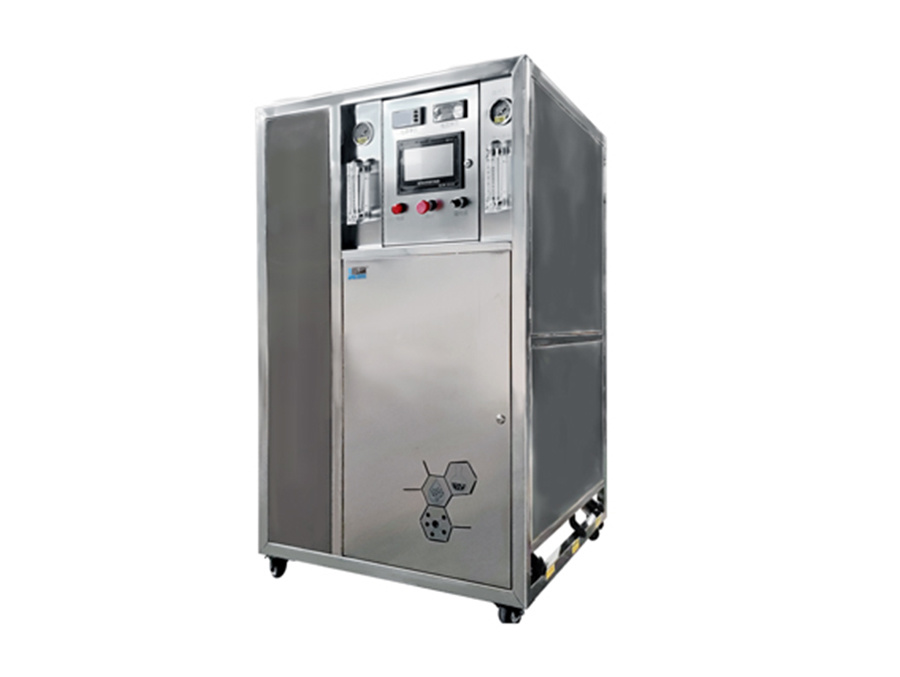
In the realm of industrial equipment and components, especially within the subcategory of water treatment devices, the laboratory ultrapure water system stands out as an essential component. These systems are designed to produce water of exceptional purity, crucial for various applications including analytical chemistry, molecular biology, and pharmaceutical testing. The importance of ultrapure water can't be overstated; impurities in water can significantly influence experimental results, leading to inaccurate data and compromised product quality.
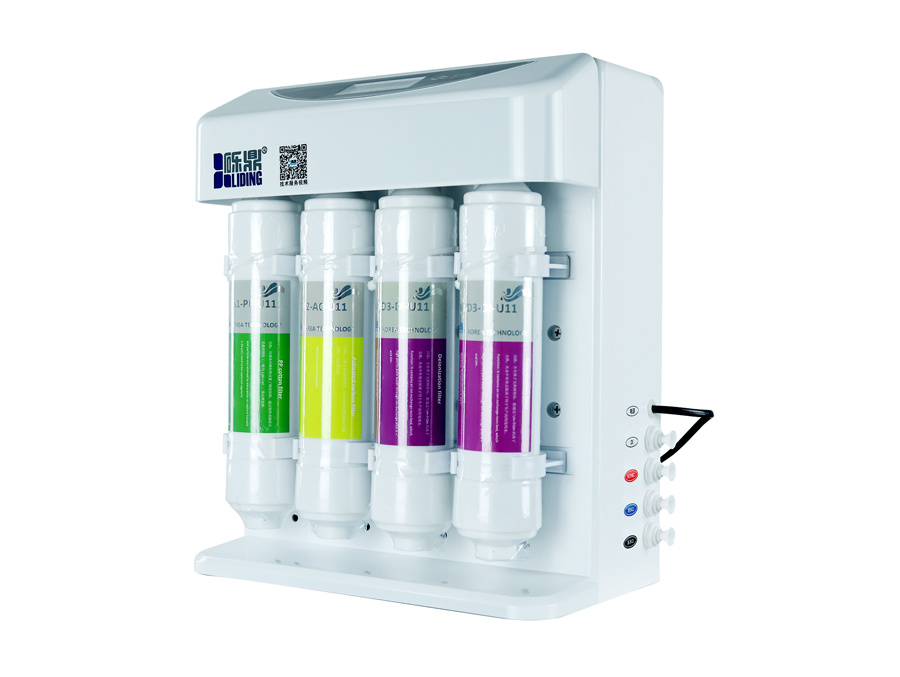
A laboratory ultrapure water system typically employs multiple purification methods to achieve the desired purity level. Common processes include reverse osmosis, deionization, and ultrafiltration. Each of these stages works collaboratively to remove contaminants such as ions, microorganisms, and organic compounds, ensuring the water meets stringent quality standards.
One of the key components of these systems is the reverse osmosis unit, which serves as a first line of defense against larger particulates and certain dissolved solids. Following this stage, deionization removes remaining ionic contaminants, making the water ideal for sensitive applications. Ultrapure water systems often incorporate additional filtration and polishing stages, utilizing advanced technologies like UV light and carbon filters to eliminate any residual contaminants.
Laboratory ultrapure water systems also come equipped with monitoring and control technologies that ensure the purity level remains consistent. Many systems include real-time monitoring sensors and alarms, providing users with immediate feedback on water quality. This feature is particularly valuable in laboratory settings where the implications of water quality are directly tied to research outcomes.
In addition to scientific applications, these systems are also beneficial in a variety of industrial processes that require high-quality water. For instance, semiconductor manufacturing and biotechnology heavily depend on ultrapure water to maintain the integrity of their processes. The reduction of contaminants helps to extend the lifespan of equipment and improve product yield.
To maximize the effectiveness and longevity of a laboratory ultrapure water system, regular maintenance and proper operation are essential. Users should follow manufacturer guidelines and perform routine checks to ensure all components are functioning optimally. This not only helps to sustain water purity but also enhances the overall efficiency of the water treatment process.
In conclusion, investing in a laboratory ultrapure water system is vital for any industry requiring high-quality water. By understanding the components and benefits of these systems, users can make informed decisions that support their operational and research needs. Whether for scientific research or industrial applications, the right ultrapure water system can significantly impact the quality and reliability of results.
A laboratory ultrapure water system typically employs multiple purification methods to achieve the desired purity level. Common processes include reverse osmosis, deionization, and ultrafiltration. Each of these stages works collaboratively to remove contaminants such as ions, microorganisms, and organic compounds, ensuring the water meets stringent quality standards.
One of the key components of these systems is the reverse osmosis unit, which serves as a first line of defense against larger particulates and certain dissolved solids. Following this stage, deionization removes remaining ionic contaminants, making the water ideal for sensitive applications. Ultrapure water systems often incorporate additional filtration and polishing stages, utilizing advanced technologies like UV light and carbon filters to eliminate any residual contaminants.
Laboratory ultrapure water systems also come equipped with monitoring and control technologies that ensure the purity level remains consistent. Many systems include real-time monitoring sensors and alarms, providing users with immediate feedback on water quality. This feature is particularly valuable in laboratory settings where the implications of water quality are directly tied to research outcomes.
In addition to scientific applications, these systems are also beneficial in a variety of industrial processes that require high-quality water. For instance, semiconductor manufacturing and biotechnology heavily depend on ultrapure water to maintain the integrity of their processes. The reduction of contaminants helps to extend the lifespan of equipment and improve product yield.
To maximize the effectiveness and longevity of a laboratory ultrapure water system, regular maintenance and proper operation are essential. Users should follow manufacturer guidelines and perform routine checks to ensure all components are functioning optimally. This not only helps to sustain water purity but also enhances the overall efficiency of the water treatment process.
In conclusion, investing in a laboratory ultrapure water system is vital for any industry requiring high-quality water. By understanding the components and benefits of these systems, users can make informed decisions that support their operational and research needs. Whether for scientific research or industrial applications, the right ultrapure water system can significantly impact the quality and reliability of results.
RELATED NEWS